The Evolution of AI and Its Impact on Existing Jobs

As we stand at the forefront of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the landscape of work as we know it. From automating mundane tasks to pioneering new ways of innovation, AI's trajectory has been nothing short of extraordinary. In this article, we delve into the evolution of AI and assess its profound impact on current jobs.
The Dawn of AI
Artificial intelligence has its roots in the mid-20th century, with the term itself being coined in 1956 during the Dartmouth Conference. Initially, AI was about replicating human intelligence in machines, leading to the creation of algorithms that could perform basic tasks. However, it wasn't until the advent of machine learning and neural networks that AI's potential started to be fully realized.
The Growth Spurt
In the past decade, we've seen an exponential growth in AI capabilities, thanks to advancements in computing power and data availability. Machine learning, a subset of AI, has enabled computers to learn from and interpret data without explicit programming. Deep learning, a more advanced form of machine learning, uses neural networks with multiple layers (hence 'deep') to make sense of vast amounts of data, leading to breakthroughs in image and speech recognition.
AI in the Workplace
AI's integration into the workplace has been met with both excitement and trepidation. On one hand, AI excels at handling repetitive and time-consuming tasks, thus freeing human workers to focus on more complex and creative work. On the other hand, the automation of certain jobs has sparked concerns about job displacement.
Automation and Efficiency
Industries like manufacturing have benefitted immensely from AI, where robots can perform precision tasks faster and more safely than humans. In the realm of services, AI chatbots provide 24/7 customer support, improving service efficiency. Even in fields like law and healthcare, AI assists with research and diagnostics, albeit under human supervision.
Job Displacement and Creation
While AI has certainly automated some jobs, particularly those involving routine tasks, it has also created new roles. AI specialists, data scientists, and ethicists are in high demand to develop, manage, and govern AI systems. Moreover, as AI takes on more of the routine work, it encourages the workforce to upskill and engage in more strategic and creative roles.
The Human-AI Collaboration
The future of work is not human vs. AI but rather human with AI. Collaborative robots, or 'cobots', work alongside humans to enhance their capabilities rather than replace them. This symbiosis allows for precision and efficiency paired with human judgment and expertise.
The Road Ahead
As AI continues to evolve, its impact on jobs will likely grow. However, history shows us that technology can be a catalyst for new forms of employment. The key is adaptability. Education systems are pivoting to include AI and technology literacy, preparing the next generation for a transformed job market.
Ethical Considerations
As we embrace AI, ethical considerations must guide its development and application. Ensuring AI systems are fair, transparent, and accountable is vital to mitigate biases and protect privacy.
Conclusion
AI's rapid development brings both challenges and opportunities. Its integration into various sectors is inevitable, but rather than viewing AI as a job stealer, it should be seen as a job transformer. By automating routine tasks, AI pushes the job market towards a future where human creativity and strategic thinking are at the forefront, promising a dynamic where AI supports humans in driving progress and innovation.
As we continue to navigate this AI-augmented landscape, it's crucial for workers, employers, and policymakers to foster a culture of lifelong learning and to ensure the ethical deployment of AI. Only by doing so can we harness the full potential of AI and secure a future where technology and humanity progress hand in hand.
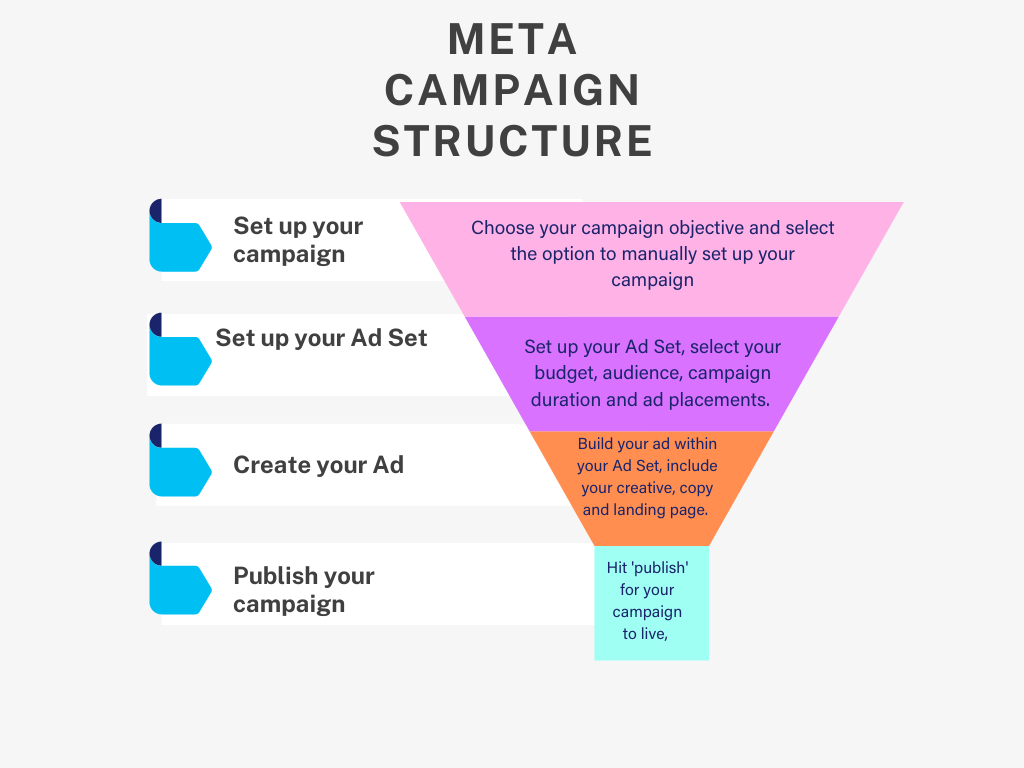
Beginning your Meta Ads Journey

Comparing Shopify Facebook Pixel Apps: Why Avantify Stands Out

The Best Facebook Pixel Apps for Shopify: A Comparative Look
Unleashing the Power of Pixels in Advertising: The Complete Guide